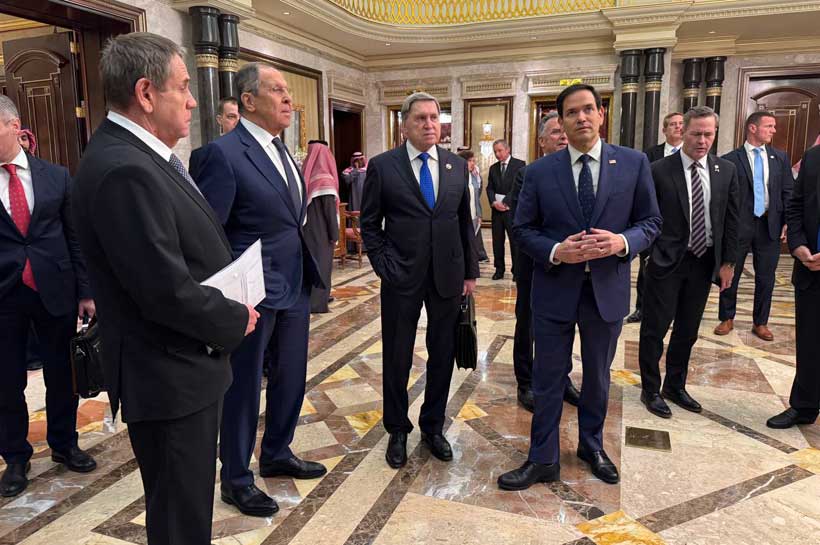
After a series of high-stakes diplomatic engagements, significant developments have unfolded in efforts to resolve the Ukraine conflict. In Saudi Arabia, a United States (US) delegation led by Secretary of State Marco Rubio, National Security Advisor Michael Waltz, and Trump’s Special Envoy to the Middle East Steve Witkoff held critical negotiations with a Russian delegation headed by Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov. However, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky met with President Donald Trump in Washington and had a heated debate on Ukraine’s policy on the war with Russia. The following analysis explores the major challenges that could complicate the peace process, stall US-Russia negotiations, and hinder efforts of the ongoing peace talks to end the Ukraine conflict.
The most critical factor shaping the future of the conflict is the territories controlled by each side. In September 2022, Russia annexed Donetsk and Luhansk, along with Zaporizhzhia and Kherson. Earlier it had also annexed Crimea in 2014. From Ukraine’s perspective, any ceasefire or peace agreement must include Russia’s complete withdrawal from all occupied territories. President Zelensky has made it clear that for hostilities to end, Russia must pull back all its troops and armed formations, restoring Ukraine’s internationally recognized borders. Additionally, Crimea remains a key sticking point. Ukraine continues to consider it illegally occupied since Russia’s annexation in 2014 and demands its full return.
Moreover, Ukrainian territories controlled by Russia have significant deposits of rare earth metals and natural resources. President Putin has offered America access to the minerals of Russian-controlled Ukrainian territories. In any case, Moscow views Ukrainian territories under their control as an integral part of Russia. But Ukraine has also gained control over parts of Russia’s Kursk region. While Russia has reclaimed most of the area, Ukraine’s continued presence remains a strategic challenge for Moscow. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has proposed a territorial exchange, offering to return Kursk in exchange for Russian-occupied Ukrainian territories. Russia has outright rejected this proposal. In any case, without deciding the future of these territories, a peace agreement would not last long.
Another decisive factor that could adversely affect peace talks is the possibility of Ukraine’s North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) membership. Russia has long opposed NATO’s expansion and views Ukraine’s potential membership as a direct threat to its security. It is important to highlight that the Biden administration backed Ukraine’s NATO bid, but the Trump administration has taken a different stance. Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth initially ruled out Ukraine’s NATO membership; however, Trump’s deputy Ukraine envoy contradicted this, stating that Ukraine’s NATO membership is still on the table. If NATO’s role in Ukraine remains unresolved, Russia may refuse to engage in meaningful negotiations, and even if an agreement is signed without deciding this matter, there is a high chance that the agreement might not be observed.
An added major challenge in achieving peace in Ukraine is ensuring that other key stakeholders accept the terms of reference (TOR) negotiated between the US and Russia. The European Union (EU) has played a significant role in the conflict, often exaggerating the Russian threat and actively supporting Ukraine through military aid. The 27-member bloc has imposed 15 rounds of sanctions aimed at crippling Russia’s war economy. Under the Biden administration, the US and the European Union (EU) pursued a unified strategy against Russia. However, Trump’s administration has taken a different approach and excluded the EU, along with Ukraine, from the direct negotiations in Saudi Arabia. This exclusion sparked concerns within the EU, leading to an emergency meeting of European leaders convened by France to discuss its response earlier to the Trump-Zelensky meeting.
During the Oval Office meeting, President Zelensky repeatedly told President Trump that without security guarantees, it would be difficult for Ukraine to accept any agreement. He also said that documents do not ensure security; rather, soldiers do. However, Trump has not spoken much about the security guarantees. Even though the mineral deal is not signed as per media outlets, the deal proposed to Zelensky acknowledges Ukraine’s efforts to obtain security guarantees needed to establish lasting peace but does not provide explicit security commitments from the US. Still, international relations experts are of the view that even explicit security guarantees are not being provided to Ukraine, but with the minerals deal, the US will have a stake in Ukraine, and these stakes can incentivize the US to uphold and defend Ukrainian security.Simultaneously, EU members have again convened in the UK, where they have pledged to maintain the flow of military aid to Ukraine, play a more proactive role, and propose an EU plan to resolve the conflict. Right now, the situation seems to deteriorate, and if TORs decided between the US and Russia are not acceptable to other stakeholders, it will further complicate the ongoing conflict.
Beyond military and political considerations, economic factors will also play a crucial role in shaping the outcome of the negotiations. A key agenda item in the discussions would be the future of economic sanctions imposed on Russia by the EU and the US. These sanctions have a significant impact on Russia’s economy, leading to a 2.1% decline in GDP in 2022. The civilian economy has been hit by soaring inflation and elevated interest rates, exacerbated by a surge in defense spending, which now accounts for nearly 7% of GDP. Additionally, sanctions and operational disruptions have created a surplus of crude oil that has forced potential production cuts and weakened one of Russia’s primary revenue streams. The resulting instability due to a fall in Russian oil exports has also fueled global market volatility, driving up oil prices amid supply concerns.
In light of persistent hostilities and deeply entrenched positions, US-Russia peace talks may mark a pivotal yet complex step toward resolving the Ukraine conflict. Territorial disputes remain a major roadblock, with neither side willing to make meaningful concessions. At the same time, Ukraine’s NATO ambitions further complicate the dialogue. Beyond bilateral discussions, the exclusion of the EU and Ukraine from initial negotiations has fueled concerns that their strategic interests are being sidelined. With European nations reaffirming their military support for Ukraine and actively seeking a more assertive role in the peace process, any agreement that disregards their involvement risks further discord. For long-lasting peace, all key stakeholders, including Ukraine, the EU, and NATO, must eventually be engaged in the process. However, given the current diplomatic deadlock, diverging geopolitical priorities, and lingering mistrust, achieving a durable resolution will require not only political will but also strategic compromises from all sides. Whether this round of talks will bring the war closer to an end or merely serve as another failed diplomatic exercise remains an open question.