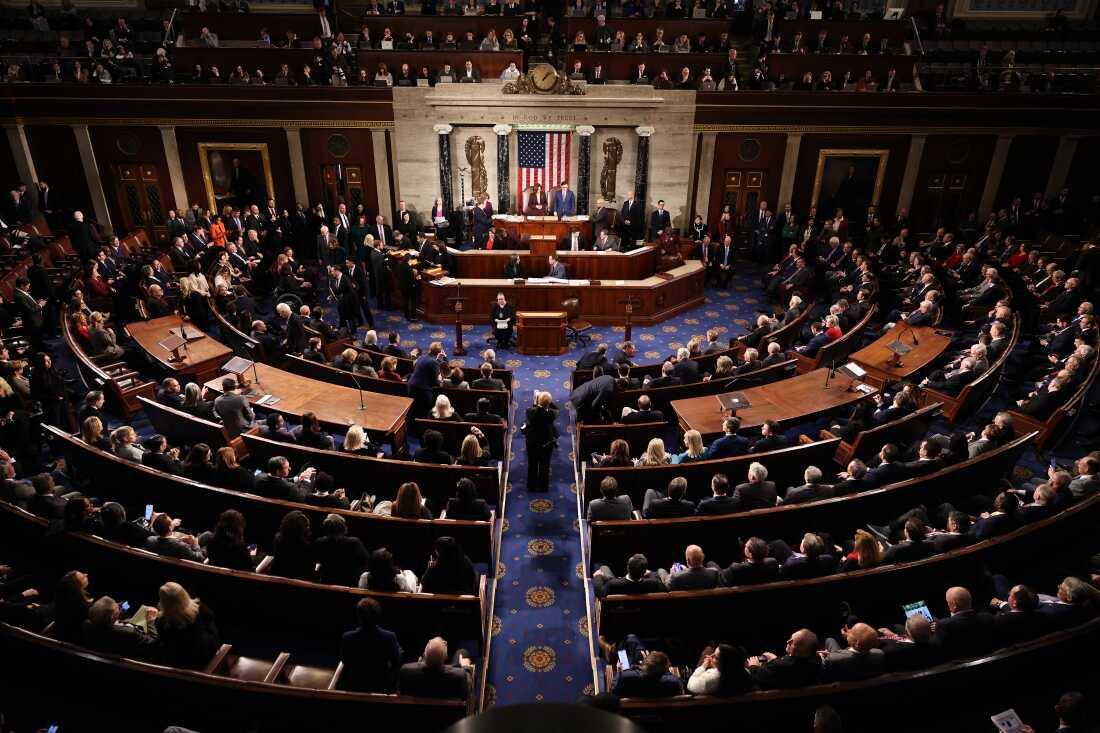
Members of Congress participate in a joint session to ratify the 2024 Presidential election at the U.S. Capitol.
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images North America
hide caption
toggle caption
Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images North America
President Trump on Tuesday will deliver his first address to a joint session of Congress since his reelection. While the speech shares many characteristics with a State of the Union address, this presentation is slightly different in nature.
Trump’s speech to Congress is expected to outline his legislative priorities for the upcoming term and highlight the work his administration has accomplished since taking office.
But since this is his first address in his second nonconsecutive term, the speech is not classified as a State of the Union.
The Constitution requires that the president “shall from time to time give to the Congress Information of the State of the Union.”
The State of the Union usually happens in January and it has evolved into a significant broadcast television event.
For the past four decades, presidents have opted not to designate their first speech to Congress as a State of the Union, instead referring to it more generally as an address to Congress.
Trump’s upcoming speech comes as he and his administration implement sweeping changes to restructure the federal government.
He currently has favorable conditions in Congress where Republicans hold a majority in both chambers.
But given the ongoing challenges posed by inflation and the controversial layoffs of thousands of federal workers as part of Trump’s extreme workforce reduction measures, it will be crucial for him to reassure Americans in his speech that relief is on the horizon.