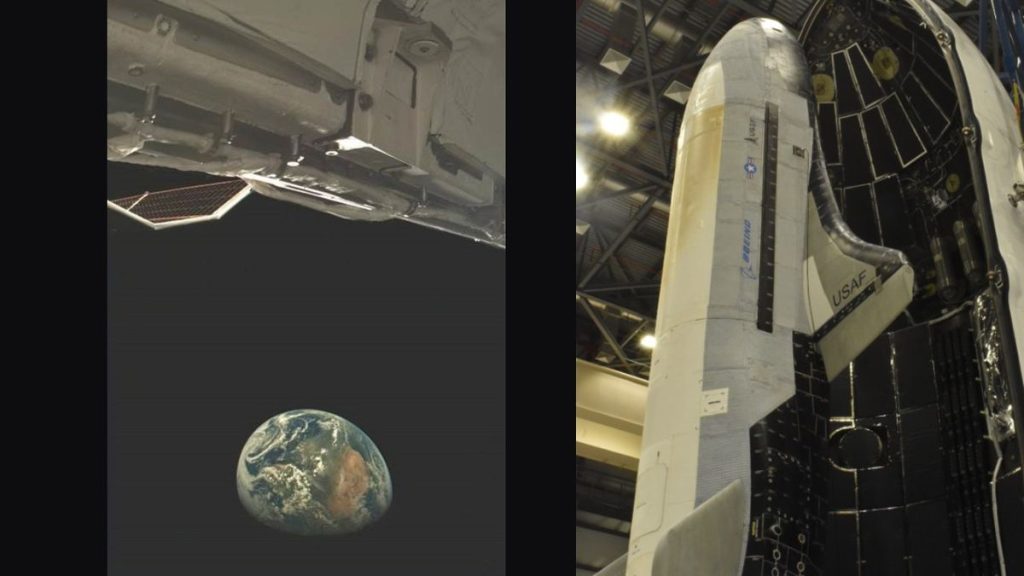
The United States Space Force just offered a rare glimpse of its shadowy X-37B space plane in orbit.
The photo, released on Thursday (Feb. 20), was taken by a camera onboard the X-37B while the secretive space plane orbited high above the African continent. One of the plane’s solar panels is visible on the left side of the photo, while what appears to be its open payload bay is visible along the top edge. The vehicle has been in orbit for well over a year now, having launched on its seventh mission on Dec. 28, 2023 atop a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
And now, the X-37B has notched another milestone with the Space Force’s release of this photo, the first-ever image of this space plane in orbit that has been shown to the public. While the photo contains scant details about the vehicle and what it’s currently testing, it offers a look at Earth far in the background, revealing just how high the vehicle is flying on its seventh mission.
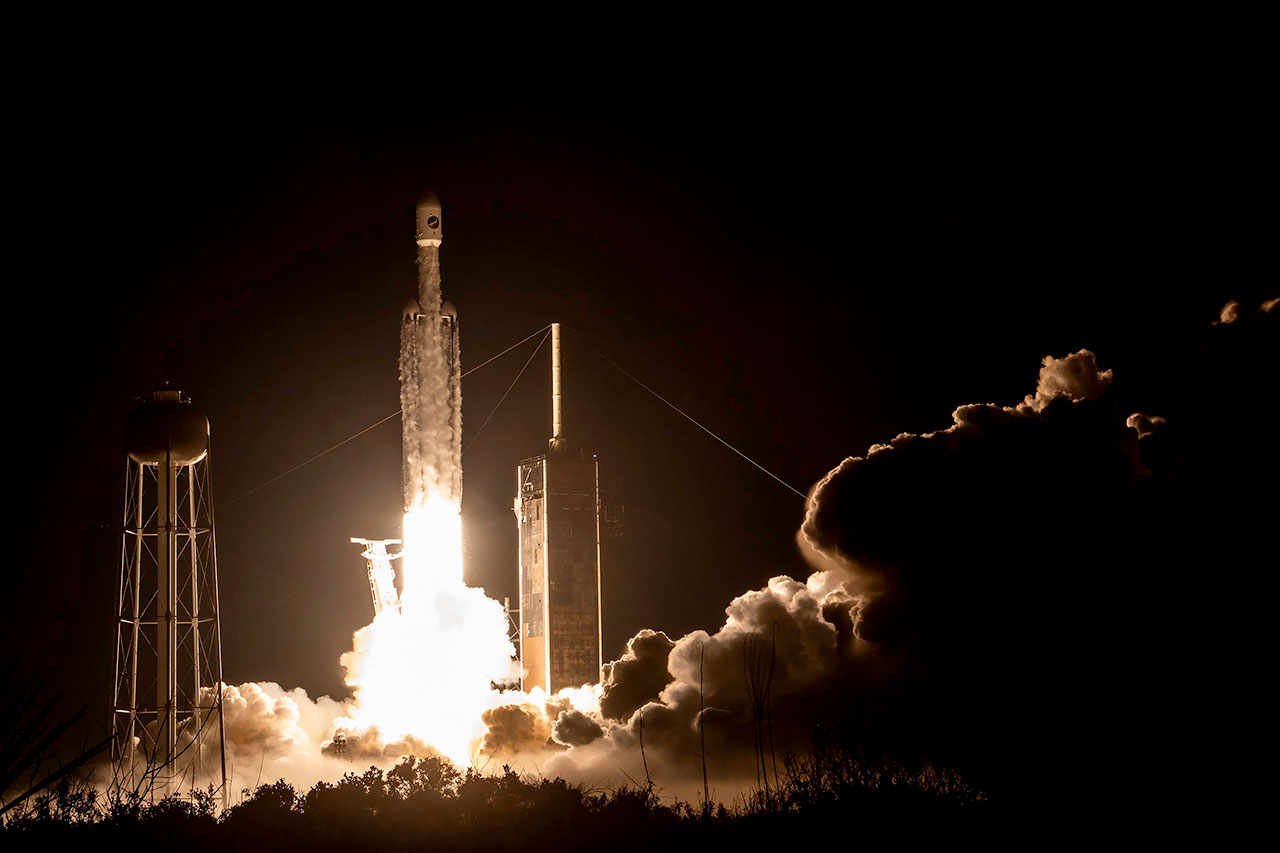
We’ve gotten only one other glimpse at the X-37B in orbit prior to this. During the livestream of its most recent launch, a brief shot of the spacecraft deploying from Falcon Heavy’s upper stage was seen while its service module was still attached:
Sneaky ! but I got it 😇During the SpaceX USSF-52 launch broadcast they showed a 2 second clip of X-37B OTV-6 with the service module during deployment on-orbit !(the big structure sticking out is FalconSat-8 btw)#X37B #OTV6 pic.twitter.com/zMf19vFvp0December 29, 2023
When the X-37B was preparing to launch on its current mission, the U.S. Space Force revealed the flight would “include operating the reusable spaceplane in new orbital regimes, experimenting with future space domain awareness technologies, and investigating the radiation effects on materials provided by NASA,” according to a Space Force statement.
Previous X-37B missions were flown in low Earth orbit, but as this photo reveals, the space plane is currently operating much farther from Earth. SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy is capable of launching payloads into geosynchronous orbit, over 22,000 miles (35,000 km) above our planet.

The X-37B recently made headlines when Space Force and Boeing, who built the vehicle, revealed that it would be testing a new “aerobraking maneuver” that uses the drag, or friction, generated by Earth’s atmosphere to change orbit more efficiently.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
According to a brief U.S. Space Force statement released alongside the photo, the image was taken while the X-37B was conducting experiments some time last year. It’s unclear if those experiments were related to the aerobraking maneuvers, although the statement does reference them.
“An X-37B onboard camera, used to ensure the health and safety of the vehicle, captures an image of Earth while conducting experiments in a highly elliptical orbit in 2024,” the Space Force’s statement reads. “As part of the X-37B’s seventh mission, the vehicle executed a series of first-of-its-kind maneuvers, called aerobraking, to safely change its orbit using minimal fuel.”
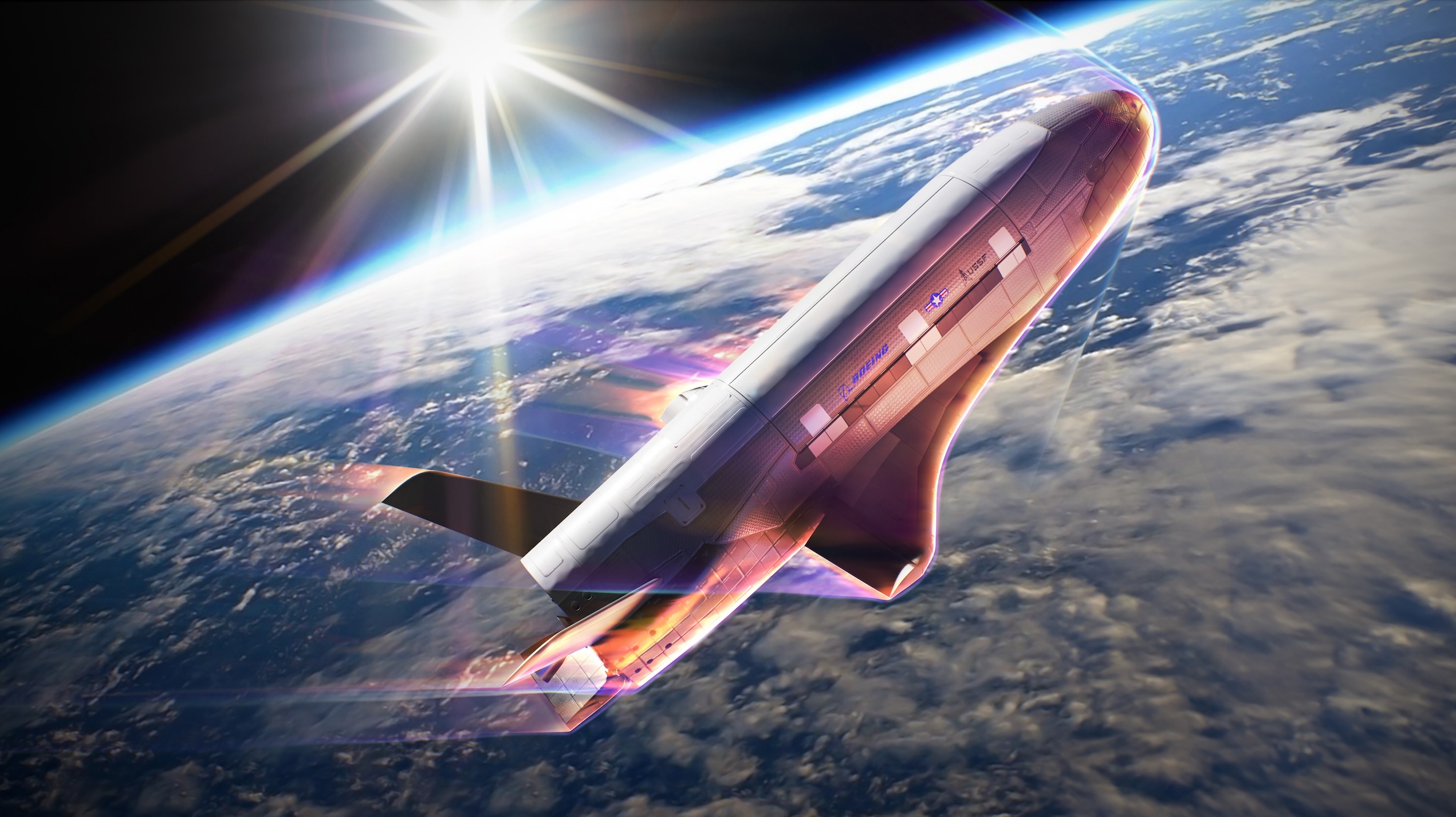

While the U.S. Space Force, and its previous operator the U.S. Air Force, have been tightlipped about what the space plane does on its lengthy missions, what is known is that the X-37B serves as a test platform for new space technologies.
So far, it has hosted payloads to test solar power beaming from space, thermal protection systems and autonomous flight capabilities. According to the Space Force, the X-37B is the “most advanced re-entry spacecraft that performs risk reduction, experimentation and concept of operations development for reusable space vehicle technologies.”
The X-37B flew for a record 908 days on its sixth mission, which ended when the landed at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 12, 2022.
Space Force does not typically publish mission timelines, so it’s unknown when the space plane might return to Earth and mark the conclusion of its seventh flight.
China is also testing its own reusable space plane. The vehicle launched on its third mission just two weeks prior to the X-37B’s most recent launch.