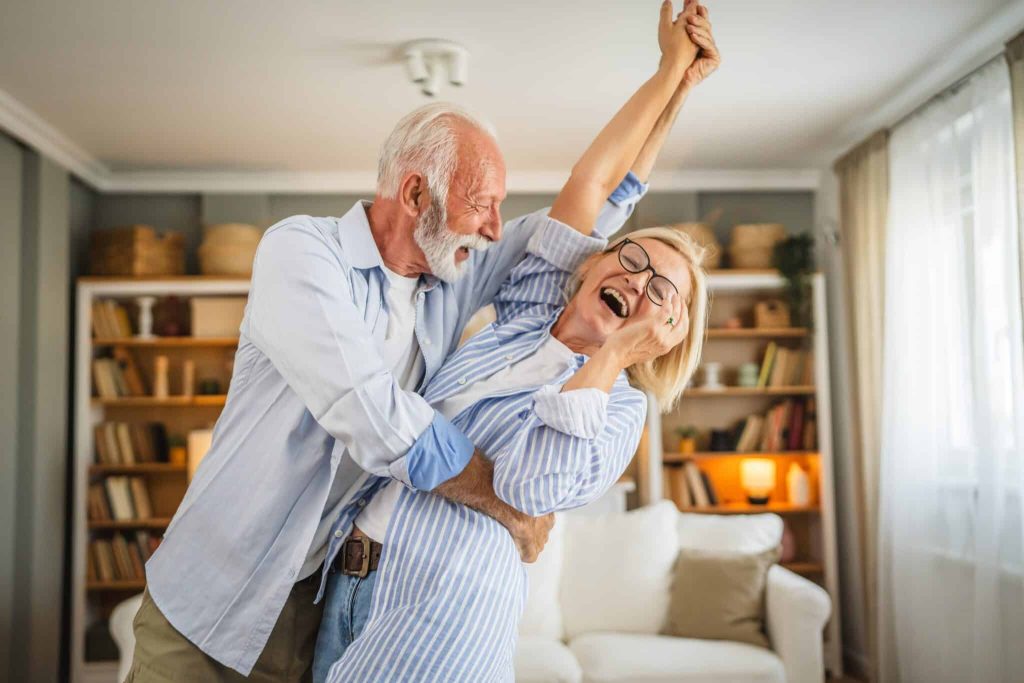
Dancing, especially with other people, can effectively reduce stress (Miljan Zivkovic/Shutterstock)
In a nutshell
- The unique combination of music, rhythm, social interaction, and physical movement in dance makes it a powerful tool for reducing stress and boosting mental health.
- Dancing with a partner or in a group enhances stress relief by providing social support, physical touch, and a sense of connection, which triggers the release of oxytocin and endorphins.
- Beyond the physical exercise, dance activates the brain’s reward system, potentially improving emotional regulation, promoting flow states, and contributing to long-term resilience.
GUILFORD, England — Feeling stressed? Instead of hitting the gym, maybe you should hit the dance floor. Chronic stress wreaks havoc on our bodies and minds, and for years, experts have been telling us to exercise as a remedy. But that doesn’t mean you have to spend hours on the treadmill. A new international study shows that dancing can help manage stress, strengthen resilience, and improve overall well-being.
Sports psychologists have been documenting the benefits of physical activity for decades, leading to countless recommendations about getting active to cope with stress. But here’s what’s been missing from the conversation: not all forms of exercise affect us the same way when it comes to taming our stress response.
A new study published in Psychology of Sport & Exercise tackles this knowledge gap by zeroing in on dance, an activity that seems to have special powers when it comes to stress relief. Researchers from several European universities collaborated across disciplines to examine why dancing might deserve special attention in our stress-fighting toolkit.
Previous research has hinted that dance activities might be particularly good at softening the blow of stress, with some researchers informally calling it a “stress vaccine.” But this new review is the first comprehensive look at what makes dance so effective, bringing together insights from psychology, neurobiology, and anthropology.
The Perfect Stress-Fighting Combination


What makes dance stand out? It’s not just another way to move your body. Dancing weaves together music, rhythm, social connection, and physical movement to create what might be the perfect recipe for stress relief.
The researchers organized their investigation around these key components: the music and rhythm that drive the dance, the partnering and social aspects of dancing with others, and the physical movement itself. Each element contributes to stress regulation on its own, but combined in dance, they create something greater than the sum of their parts.
Music itself works wonders on our stress levels. The review found plenty of evidence that just listening to music can lower anxiety and help people relax. When we hear music, our brain’s reward system kicks into gear, releasing feel-good chemicals like dopamine and endorphins while potentially dialing down cortisol, our body’s main stress hormone.
One fascinating study discovered that dancing to “groovy” music produces a state of flow, that wonderful feeling of being completely absorbed in what you’re doing, which didn’t happen when people merely listened to the same music without dancing.
Brain research shows that music lights up the circuits involved in pleasure and reward, while also activating areas that regulate our body’s balance and stress response. Our love of rhythm might even have evolutionary roots, potentially serving as an ancient mechanism that fostered cooperation and social connections among our ancestors.
The Power of Dancing Together


Dancing with someone else adds another layer of stress-busting power. The review notes that dancing with a partner or in a group seems more beneficial than dancing solo. Social support and physical contact can notably reduce our physiological stress response. Touch, especially, helps buffer stress by triggering pathways in the brain that release oxytocin, sometimes called the “love hormone,” along with endorphins.
Looking at dance through an anthropological lens shows how it has historically brought people together, building social bonds and expressing emotions collectively. Across cultures, dance creates shared spaces for healing and developing group coping strategies. When people move in sync while dancing, it fosters a sense of unity and connection that can be comforting during tough times.
Dance’s physical movement works against stress much like other exercises do but with some particular advantages. All physical activity boosts endorphins and dopamine, helps regulate stress hormones, and promotes overall health. But dance movement, with its rhythmical quality, seems to offer something extra.
One study found that dance training improved cortisol regulation in older adults more effectively than regular aerobic exercise, even though only the aerobic exercise group showed improved fitness. This suggests that dance affects our stress-response system through more than just physical conditioning.
Beyond Traditional Exercise
The evidence suggests dance deserves special consideration as a stress-management tool. Its combination of features works on multiple levels simultaneously: reducing isolating feelings, building resources like self-esteem and social support, potentially dampening our immediate stress reactions, and boosting overall well-being.
This doesn’t mean you should ditch your regular workout routine if it’s working for you. But adding some form of dance, whether it’s a structured class, social dancing, or just moving to music at home, might give you stress-fighting benefits that other exercises can’t match.
Paper Summary
Methodology
The researchers initially attempted a systematic literature review on dance and stress but found limited studies directly examining this relationship. They pivoted to a narrative review approach, incorporating research from psychology, neuroscience, and anthropology. Their team organized findings into three main categories: music and rhythm; partnering and social contact; and movement and physical activity. For each section, they presented evidence from psychological studies, neurobiological research, and socio-cultural perspectives.
Results
The review revealed that music activates the brain’s reward system while potentially lowering stress hormones. When combined with movement in dance, it creates unique states like “flow” that aren’t achieved through listening alone. Studies showed dancing with partners produces more positive effects than solo exercise, with synchronization promoting feelings of connection. The physical aspect of dance contributes to stress regulation through multiple pathways, including boosting endorphins and improving overall health. Notably, dance training improved cortisol regulation better than traditional aerobic exercise, suggesting benefits beyond mere fitness improvements.
Limitations
The authors acknowledge several constraints. Few studies directly examine recreational dance and stress, forcing them to broaden their approach. Their narrative review methodology lacks the systematic rigor that would minimize selection bias. They couldn’t address all relevant dance characteristics, omitting factors like communication, body awareness, and emotional expression. “Dance” encompasses many styles from structured routines to spontaneous movement, a complexity they couldn’t fully explore. Finally, it’s difficult to isolate which specific components (music, social contact, or movement) drive particular benefits.
Discussion and Takeaways
The researchers emphasize this review provides a first step toward understanding the complex relationship between dance and stress regulation. They argue dance uniquely integrates mind, body, and cultural elements, making it particularly effective for building coping skills and resilience. For the field of exercise psychology, they recommend moving beyond the traditional focus on exercise intensity to consider social components, touch, and musical elements. Understanding the mechanisms behind different exercise types could lead to more personalized and effective stress management recommendations.
Funding and Disclosures
The paper does not mention any specific funding sources or financial conflicts of interest.
Publication Information
The paper, “Dance and stress regulation: A multidisciplinary narrative review,” was authored by Sandra Klaperski-van der Wal, Jonathan Skinner, Jolanta Opacka-Juffry, and Kristina Pfeffer. It was published in Psychology of Sport & Exercise (volume 78, Article 102823) in 2025. The authors are affiliated with Radboud University (Netherlands), the University of Roehampton, the University of Surrey (UK), and the University of Southern Denmark.